Characterization method of powder particle size and particle size distribution
The characterization methods of powder particle size and particle size distribution mainly include: sieving method, microscopic analysis method, deposition method, laser method, electronic sensing technology, and X-ray diffraction method. At present, the most commonly used particle size analysis method is to use laser particle size analyzer.
Particle morphology includes shape, surface defects, roughness, etc. Therefore, a correct understanding of the initial powder is the key to understanding the observed powder morphology characteristics in the later process. According to the interaction between the particle beam and the powder particles, the following three methods are mainly used for the characterization of the powder surface morphology:
(1) Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES): The disadvantage is that the charge accumulation on the surface of the powder can easily lead to inaccurate results.
(2) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS): It can be used to determine the oxidation state of surface atoms.
(3) Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS): suitable for qualitative elemental analysis, but the quantitative analysis results are unreliable.
The main application instruments are: scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, scanning probe microscope, etc.
Powder specific surface area test method
The specific surface area testing methods are mainly divided into adsorption method and air permeability method. Among them, the adsorption method is more commonly used and has higher precision; the air permeability method is to determine the specific surface area of the powder according to the different air permeability rates, and the specific surface test range and accuracy are very limited.
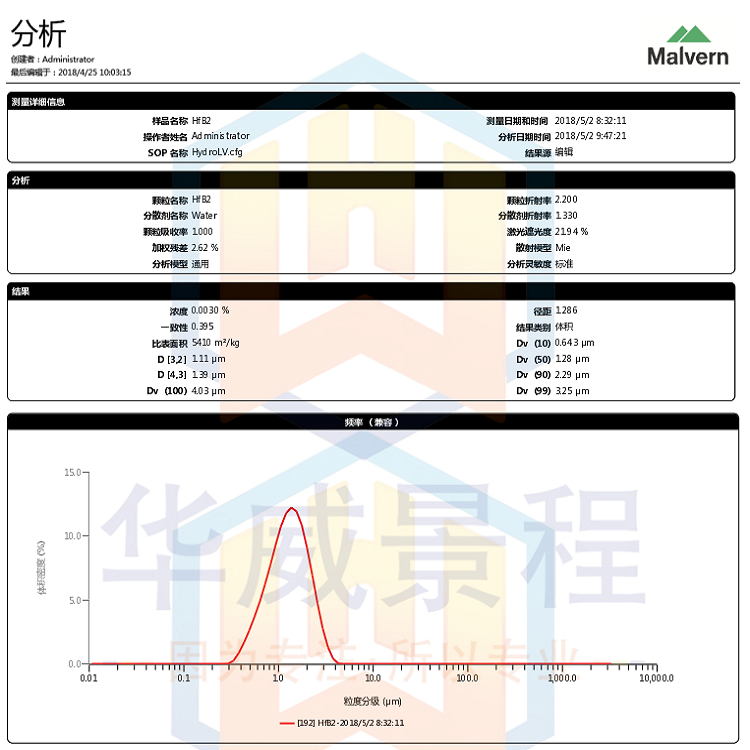
Particle size distribution
Laser particle size analyzer is the most commonly used method at present to measure the particle size distribution of powder to characterize the dispersion. Firstly, the scattered light energy distribution corresponding to particles with various diameters within the measurement range of the instrument is calculated, and the corresponding particle size distribution is obtained through appropriate numerical calculation. The smaller the average particle size of the particles, the better the dispersibility of the particles, that is, there is no or only a small amount of soft agglomeration.
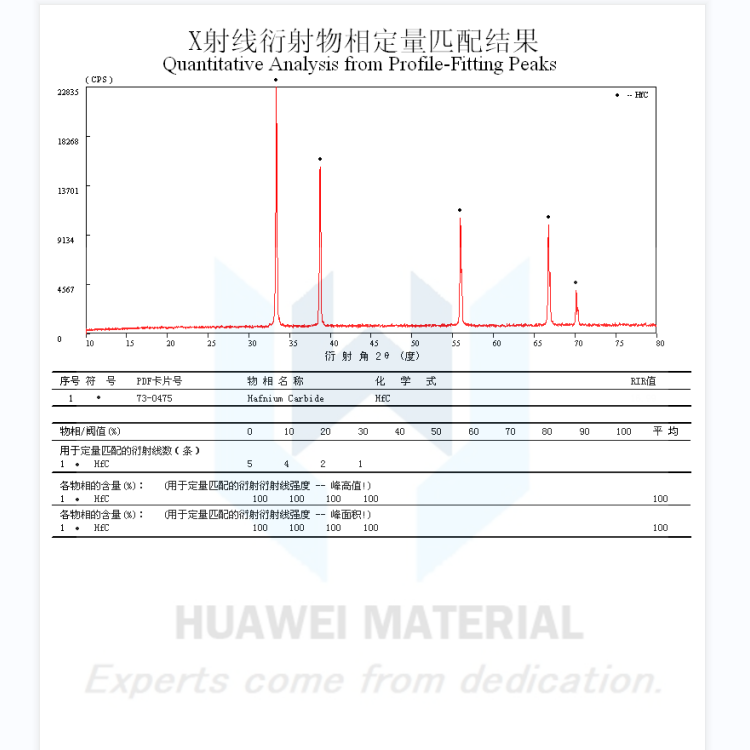
Powder chemical composition analysis is generally by means of scanning electron microscope and X-ray diffractometer and other instruments.